Helping enterprises unleash the full potential of IoT
by Nir Elron | November 30, 2023
While the changes brought by eSIM became transformative for the telecommunication industry, its technical capabilities described in our previous blog post also have a significant impact on the IoT market. eSIM has benefits for all players in the market: device manufacturers, enterprises that deploy and manage fleets of IoT devices, and the connectivity solutions providers.
However, the development of the market and mass adoption of eSIM were hindered by the limitations of over-the-air provisioning architectures: the M2M was rather complex and Consumer not quite suitable for IoT devices without a user interface. The new GSMA IoT eSIM remote provisioning standard (SGP.32 specification) was created to eliminate these hurdles, and now it is expected to substantially accelerate further growth of connected devices use and eSIM adoption. According to Juniper Research forecast, IoT connections using eSIM technology will reach a volume of 195 million by 2026, up from 22 million in 2023 — a 780% growth over the next three years globally.
The new specification greatly simplified mechanism enables connectivity provisioning of the eSIM, unlocking all of its value. The ability to choose a provider based on any business criteria at the most appropriate time is a big advantage of eSIMs, providing flexibility in all business cases, including the most challenging ones such as B2B2B, where the original manufacturer doesn’t know where the device will be deployed by the end customer in a chain.
It is also possible now to address all device types using eSIM, including constrained devices, such as NB-IoT devices, that could not be addressed before. This is critical for feasibility of IoT projects involving devices with a long lifecycle that need long-term connectivity support.
With less technical challenges related to eSIM usage, OEMs can benefit from overall expansion of service offering that will bring more options of device connectivity. Better commercial terms and new partnerships may significantly affect IoT deployment costs and timing. The new specification also took the best from previous standards in terms of security.
Thanks to all these technological innovations, eSIM can bring to life the promise of massive IoT by giving OEMs and enterprises a number of major benefits.
What is an advantage of eSIM to manufacturers and businesses:
Simplified management
One of the main benefits of eSIM for enterprises that deploy IoT devices is flexibility and convenience of management. The ability to remotely activate connected devices, monitor and control their data usage and change mobile network providers on the fly at any point in their lifecycle makes IoT deployments easier and more cost-efficient. For example, a change of local provider that before would have taken weeks and require changing SIMs in the devices manually, now can be done within hours.
This applies to scaling as well: no matter how many devices need to be connected and where, they can be activated and provisioned remotely. And all this allows to save costs and time on device maintenance, too – because it eliminates the need for technicians handling devices in the field changing SIMs if, for example, the contract is expired.
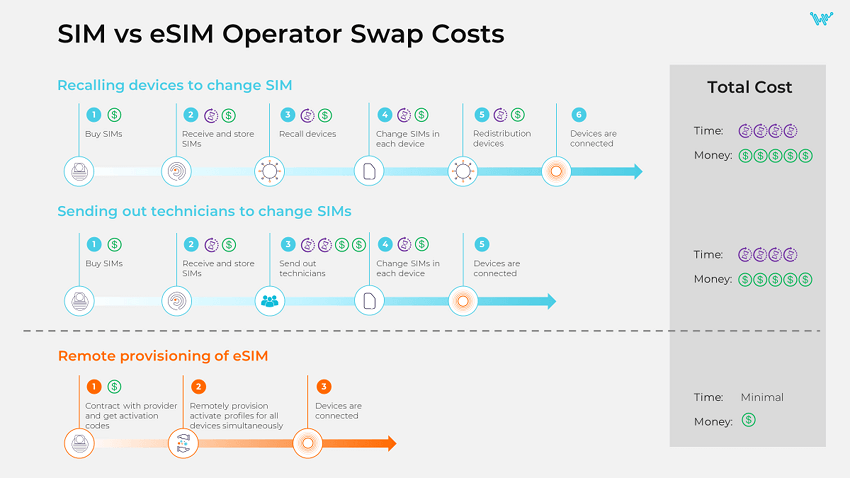
SIM vs eSIM Operator Swap Costs
Futureproof deployments
The bigger your deployment’s scale and the more diversity of IoT devices, the more vulnerable it is to changes in standards and protocols, which is inevitable with time. Just recently seven million UK energy customers were warned that their smart meters could become useless when the 2G and 3G phone networks are switched off. These devices either will need to be replaced or will require new SIM cards.
By using eSIMs in installations of smart meters and other IoT devices, both stationary and moving, enterprises can ensure that their deployments are protected from such costly upgrades when standards, provider’s network settings, or simply data plans have changed.
Having once deployed IoT devices, OEMs and enterprises won’t ever have to physically handle them again for the rest of their lifecycle. Where previously they would need to be manually updated, repealed or replaced, now profile switching and all necessary updates will be done remotely, which also helps save a lot on workforce and operations.
Compliance with regulations
Many companies rely on roaming to deploy their connected devices globally. However, in some countries permanent roaming is prohibited, while others effectively ban it by requiring the connectivity to be provided by a locally registered operator.
If there are restrictions on permanent roaming, to remain connected after a certain period of time (usually 2-3 months) a device must use a SIM or eSIM profile from a local operator. Consumer devices rarely need to roam that long, and it is easy to buy and insert a local SIM, while for IoT device it may become a serious problem, especially if the device is deployed in hard-to-reach location or is hard to manipulate.
Along with restrictions on permanent roaming there may be other regulations that have impact on IoT deployments. Be it data privacy and data sovereignty legislation or industry-specific regulation, such as e-Call, an automatic call generated from a vehicle in case of a road accident, all of them require connectivity localization.
Using an eSIM solves all these problems due to its remote provisioning capabilities that allow to remotely upload a profile from a local provider and switch between connectivity profiles, eliminating the risk of incompliance with all kinds of local regulations.
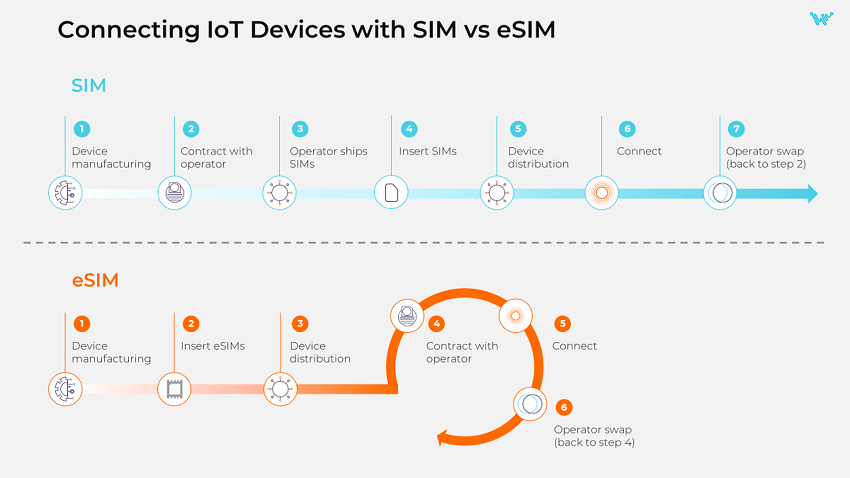
Connecting IoT devices with SIM vs. eSIM
Simplified production and distribution of devices
Before there was eSIM, shipping connected products to various markets meant either having multiple production lines to make different versions of the same product with different carrier SIMs or managing a process of buying and keeping the inventory of local SIMs and swapping them when devices reach their destination. This can significantly increase the cost of manufacturing, supply and logistics.
With eSIM, device manufacturers don’t need to worry about specific SIMs for specific regions at the stage of production and shipping and can use a single stock keeping unit (SKU) eSIM for all its devices. It considerably simplifies manufacturing and supply chain management and reduces costs.
Webbing’s solution
Our eSIM solution, WebbingCTRL, ensures failover connectivity with the capability of using multiple mobile carrier profiles, easily changing carriers at any time with zero integration, and an option to fall back from a failing profile to a different profile without any need to communicate with a remote server. Webbing’s eSIM is aligned with the GSMA SGP.32 IoT eSIM specification, which means it will be fully compatible with the new standard when it becomes ubiquitous.
WebbingCTRL enables organizations to remotely add, remove, and swap operators for any number of IoT deployments immediately without operator integration or collaboration. It also provides a centralized way to manage eSIMs/SIMs lifecycle and profile inventory, as well as visibility into device data usage. Companies can set up business rules that would allow devices to change the serving operator automatically under specific conditions, such as location, country, loss of connectivity or even after a certain amount of time. WebbingCTRL platform can work with both SGP.32 and SGP.22 standards, and also supports M2M devices for relevant use cases. It provides a single pane of glass to manage all devices deployed regardless of standards used. Visit our website to discover how WebbingCTRL can transform the way you manage your IoT deployments.
Webbing’s partner network of over 600 mobile operators worldwide guarantees global coverage. Our connectivity solution gives access to several carriers’ network at any location, ensuring continuous connectivity without having to contract with multiple operators.
Webbing’s distributed core network with local breakouts, multiple network solution, and data server redundancy provides connectivity stability and low latency. It also allows to easily comply with local regulators’ requirements and helps to adapt to any changes in legislation. Besides, it gives enterprises the ability to quickly scale their deployments or adjust their existing fleet management to any business scenarios.
More than 1 million WebbingCTRL eSIMs/SIMs have already been deployed globally since its release in April 2022.
Contact us today to learn how WebbingCTRL can support your organization’s connectivity strategy with a customized solution.




